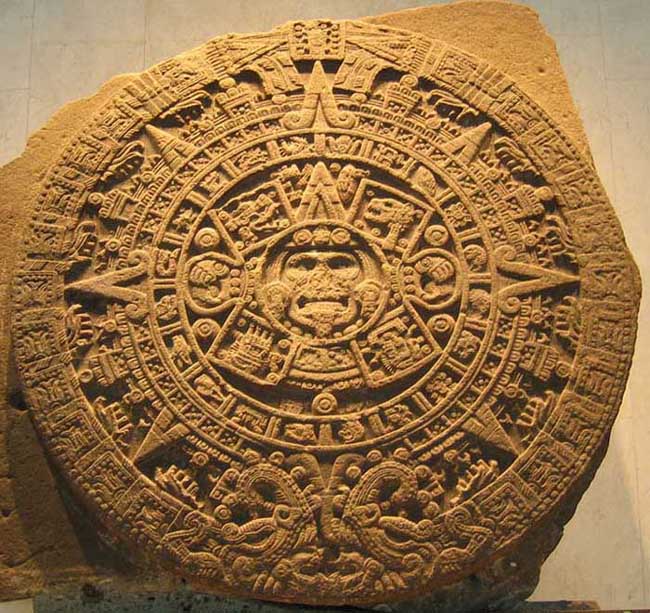

The Aztec calendar was the calendar of the Aztec people of Pre-Columbian Mexico. It is one of the Mesoamerican calendars, sharing the basic structure of calendars from throughout ancient Mesoamerica. This calendar is recorded as a carving on the Aztec Calendar Stone currently found in the National Museum of Anthropology and History located within Chapultepec Park, Mexico City.
The calendar consisted of a 365 day calendar cycle and a 260 day ritual cycle. These two cycles together formed a 52 year "century", sometimes called the "Calendar Round".The calendric year began with the first appearance of the Pleiades asterism in the east immediately before the dawn light.
Every month had its name, and the days of the month were numbered from one to twenty. The days of the last month, Nemontemi, were numbered from one to five.The box at the top of the stone contains the stone's year of creation, in this case 1479 CE.
The solar calendar of 365 days was inseparable from the Sacred Round, or Sacred Almanac. The priests used this ritual calendar of 260 days called Tonalpohualli primarily for divinatory purposes. The method of naming the individual days consisted in the combination of twenty pictorial signs with the numbers one to thirteen. Each of the day signs also bears an association with one of the four cardinal directions.The 20 day signs are depicted in the calendar image to the right. They are arrayed in a circle surrounding the central face.
The original Aztec Calendar is a 12', massive stone slab, carved in the middle of the 15th century. Many renditions of it exist and have existed through the years and throughout Mexico.
Historically, the Aztec name for the huge basaltic monolith is Cuauhxicalli Eagle Bowl, but it is universally known as the Aztec Calendar or Sun Stone. It was during the reign of the 6th Aztec monarch in 1479 that this stone was carved and dedicated to the principal Aztec deity: the sun. The stone has both mythological and astronomical significance. It weighs almost 25 tons, has a diameter of just under 12 feet, and a thickness of 3 feet.
On December 17th, 1790 the stone was discovered, buried in the "Zocalo" (the main square) of Mexico City. The viceroy of New Spain at the time was don Joaquin de Monserrat, Marquis of Cruillas. Afterwards it was embedded in the wall of the Western tower of the metropolitan Cathedral, where it remained until 1885. At that time it was transferred to the national Museum of Archaeology and History by order of the then President of the Republic, General Porfirio Diaz.

Xiuhmolpilli commemorative sculpture marking the completion of the fifty-two-year cycle. Every 52 years the tonalpohualli and the xiuhpohualli calendars would align. This marked what was known as a Mesoamerican "century." Every one of these centuries was marked by xiuhmolpilli - Binding Up of the Years or the New Fire Ceremony. This was a festival that lasted 12 days and included fasting as a symbol of penitence. At the beginning of this festival all the lights in the city were extinguished - people let their hearth fires go out. Then on midnight of the 12th day of the festival, a prisoner was taken to the priest. The priest would watch in the night sky for the star of fire to reach the zenith. Once it did, the priest would remove the heart of this man, and replace it with a piece of wood, that was laid on a piece of turquoise. This is where the priest would start the new fire that would once again light the city.
No. | Name of Month | Patron Gods and Rituals |
| I. | Atlacacauallo (ceasing of water) | Tlaloc, Chachihutlicue Children sacrificed to water gods |
| II. | Tlacaxipehualiztli (flaying of men) | Xipe-Totec Gladiatorial sacrifice; dances by priest wearing the flayed skin of victims |
| III. | Tozoztontli (little vigil) | Coatlicue, Tlaloc Flayed skins buried, child sacrifices |
| IV. | Hueytozoztli (great vigil) | Centeotl, Chicomecacoatl Blessing of new corn; maiden sacrificed |
| V. | Toxcatl (dryness) | Tezcatlipoca, Huitzilopochtli Impersonators of these major gods sacrificed |
| VI. | Etzalcualiztli (meal of maize & beans) | Tlaloques Impersonators of water deities sacrificed by drowning; ritual bathing and dances |
| VII. | Tecuilhuitontli (small feast of the lords) | Huixtocihuatl, Xochipilli Impersonators of the gods sacrificed; ceremony of salt workers |
| VIII. | Hueytecuihutli (great feast of the lords) | Xilonen Feast for goddess of young corn, lords offer gifts and feast for commoners |
| IX. | Tlaxochimaco (birth of flowers) | Huizilopochtli All the gods festooned with garlands; feasting on corn-meal cakes and turkey |
| X. | Xocotlhuetzin (fall of fruit) Hueymiccaihuitl (great feast of the dead) | Xiuhtecuhtli Ceremonial pole climbing competition Sacrifice to fire gods by roasting victims alive |
| XI. | Ochpaniztli (sweeping of the roads) | Tlazolteotl Sweeping of house and roads; mock combat |
| XII. | Teoleco (return of the gods) | Tezcatlipoca Ceremonies welcoming gods returning to earth; ceremonial drunkenness, sacrifices by fire |
| XIII. | Tepeihuitl (feast of the hills) | Tlaloc Ceremonies for mountain rain gods; human sacrifices and ceremonial cannibalism |
| XIV. | Quecholli (precious feather) | Mixcoatl-Camaxtli Ritualistic hunt following fast; sacrifice of game and ceremonial feasting |
| XV. | Panquetzaliztli (raising of the banner) | Huitzilopochtli Homes and fruit trees decorated with paper banners; race-procession; massive sacrifices |
| XVI. | Atemoztli (water decends) | Tlaloc Festival honoring water gods; children and slaves sacrificed |
| XVII. | Tititl (stretching) | Llamatecuhtli Sympathetic magic to bring rain; women beaten with straw-filled bags to make them cry |
| XVIII. | Izcalli (resuscitation) | Xiuhtecuhtli Image of god made from amaranth dough; feasting on tamales stuffed with greens |
| Nemontemi (empty days) | Five unlucky days; no rituals, general fasting |
The tonalpohualli (count of days) was the sacred almanac of the Mexicas. This ritual calendar was registered in the tonalamatl (book of days), a green-fold bark paper or deerskin codex from which a priest (called tonalpouque) cast horoscopes and predicated favorable and unfavorable days of the cycle. The almanac year comprised of 260 days, each of which was assigned a date by intermeshing one of 20 day-signs, represented graphically with a glyph, and a number from 1 to13, represented by dots so that no two days in the cycle could be confused. The almanac year was thus made up of 20 13-day weeks, with the first week beginning on 1-Crocodile and ending on 13-Reed, the second week running from 1-Ocelot to 13-Deaths' Head and so on. A god or goddess was believed to preside over each day-sign, as shown in the following chart.

Tonatiuh's Face is the face of the sun, Lord of Heaven, around which takes place all daily and periodic phenomena. The crown, nose-pendant, ear-rings and necklace are magnificent, as must be the ornaments characteristic of this deity. The hair is blond, due to the golden appearance of the sun. The wrinkles on the face show age and maturity. And the tongue, stuck out is the form of an obsidian knife, indicates that the diety demands to be fed with blood and human hearts.
First Ring - from Center. Four Olin representing the Earthquake Epoch or Sun. The four epochs represented inside the square portions of this symbol correspond to the four previous epochs also called suns.
Second Ring - The second ring from the center is composed of 20 named days contained in one month, also used for naming years. Each year starts on one of four of these 20 days.

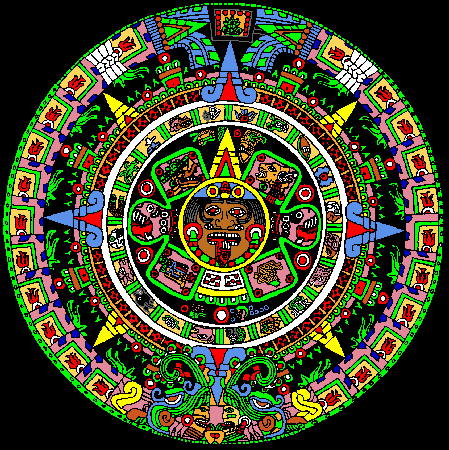
Snake - Coatl
Lizard - Cuetzpallin
House - Calli
Wind - Ehecatl
Crocodile - Cipactli
Flower - Xochitl
Rain - Quiahuitl
Flint - Tecpatl
Movement - Ollin
Vulture - Cozcacuauhtli
Eagle - Cuauhtle
Jaguar - Ocelotl
Cane - Acatl
Herb - Malinalli
Monkey - Ozomatli
Hairless Dog - Itzquintli
Water - Atl
Rabbit - Tochtli
Deer - Mazatl
Skull - Miquiztli
Third Ring - Sun Rays - Chalchihuite Ornaments - Splashed Blood Symbols
Outer Ring - Dedication Plate - Herbs with Buds - White Scrolls - Flame Sign - Xiucoatl's Tail
The two calendars were was basically similar. The ritual day cycle was called Tonalpohualli and was formed, as was the Mayan Tzolkin, by the concurrence of a cycle of numerals 1 through 13 with a cycle of 20 day names, many of them similar to the day names of the Maya.
Where the Aztec differed most significantly from the Maya was in their more primitive number system and in their less precise way of recording dates. Normally, they noted only the day on which an event occurred and the name of the current year. This is ambiguous, since the same day, as designated in the way mentioned above, can occur twice in a year. Moreover, years of the same name recur at 52-year intervals, and Spanish colonial annals often disagree as to the length of time between two events.
Other discrepancies in the records are only partially explained by the fact that different towns started their year with different months. The most widely accepted correlation of the calendar of Tenochtitlan with the Christian Julian calendar is based on the entrance of Cortes into that city on November 8, 1519, and on the surrender of Cuauhtemoc on August 13, 1521. According to this correlation, the first date was a day 8 Wind, the ninth day of the month Quecholli, in a year 1 Reed, the 13th year of a cycle.
The Mexicans, as all other Meso-Americans, believed in the periodic destruction and re-creation of the world. The "Calendar Stone" in the Museo Nacional de Antropologia (National Museum of Anthropology) in Mexico City depicts in its central panel the date 4 Ollin (movement), on which they anticipated that their current world would be destroyed by earthquake, and within it the dates of previous holocausts: 4 Tiger, 4 Wind, 4 Rain, and 4 Water.
The Aztec calendar kept two different aspects of time; tonalpohualli and xiuhpohualli. Each of these systems had a different purpose. The tonalpohualliwas the 'counting of days.' It originated by ancient peoples observing that the sun, crossed a certain zenith point near the Mayan city of Copan, every 260 days. So this first system is arranged in a 260-day cycle. These 260 days were then broken up into 20 periods, with each period containing 13 days, called trecenas. Each period was given the name of something that was then shown by a hieroglyphic sign, and each trecena was given a number 1-13. Each trecena is also thought to have a god or deity presiding over each of the trecena. They kept these counts in tonalamatls, screenfold books made from bark paper. The Aztecs used this as a religious calendar. Priests used the calendar to determine luck days for such activities as sowing crops, building houses, and going to war.
The xiuhpohualli was the 'counting of the years.' This calendar was kept on a 365-day solar count. This was also the agricultural and ceremonial calendar of the Aztec state. It was divided into 18 periods, with each period containing 20 days, called veintenas. This left five days that were not represented. These were called "nemontemi." These were the five transition days between the old and the new year, and were considered days of nothing. This was a time of festivals. People came to the festivals with their best clothes on, and took part in singing and dancing. This is also when the priest would perform sacrifices, most of these sacrifices were human, but others were preformed on animals and fruit.
The solar year was the basis for the civil calendar by which the Mexicas (Aztecs) determined the myriad ceremonies and rituals linked to agricultural cycles. The calendar was made up of 18 months, each lasting 20 days. The months were divided into four five-day weeks. The year was rounded out to 365 days by the addition of the five-day nemontemi (empty days), an ominous period marked by the cessation of normal activities and general abstinence. The correlation of dates in the Gregorian calendar is uncertain, although most authors on the subject affix the beginning of the Aztec year to early February. A variety of sources were consulted in developing the following chart of some of the ritualistic activities associated with each month.
Many of the Aztecs' religious ceremonies, including frequent human sacrifices, were performed at the Great Temple, located in the center of their capital city of Tenochtitlan.




0 comments:
Post a Comment